S1B - 2022
Sunday, March 20, 2011
Work Power and Energy
(1) Stress (2) Energy (3) Displacement (4) Force (5) Work
(6) Pressure (7) Torque (8) Weight (9) Velocity
A1. Stress & Force, Energy & Work, Force & Weight
Q2 In the above question, Select the odd one ? Write the uses of dimensional analysis ?
A2. odd one is Torque because it is related to circular motion.
Uses of dimensional analysis are
I. Check the correctness of an equation
II. Derive an equation relating to two or three physical quantities
III. Find dimension of constants in an equation
IV. Convert unit from one system to another.
Motion in one dimension
(a) How long will it take to reach the ground ?
A1.
Here Initial velocity u = 10 m/s ( Positive , since direction of initial motion is positive)
Displacement , S = - 500 m (towards downward - against initial motion direction)
Acceleration (due to gravity) , a = - 9.8 m/s2 (also downwards - against initial motion direction)
Use equations: S = ut + 1/2 a t2
See answer as : t = 11.12 seconds
Thursday, March 17, 2011
Friday, March 11, 2011
Waves
Young’s principle of superposition of waves
When two or more waves travel in a medium, along a straight line, simultaneously, then net displacement of any particle is the algebraic sum of displacement produced by the individual waves separately.
This principle work good for mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves, provided their amplitude is not very large.
Bounded Medium:
A medium bounded by definite boundaries. Boundary can be of two types
[1] Free boundary
[2] [2] Rigid or Fixed boundary

Let both end of a string be Free. Transverse wave / pulse propagates along the string is get disappear while reaching at the other end. Mean time, another pulse appear to come back from the free end. Here there is no change in phase ( π = 0) of the reflected pulse.
If equation for incident wave
y = A sin (wt - kx)Then the equation of wave reflected from the free ind will be
y = A' sin (wt + kx)
Wave / pulse reflected from Free boundary.
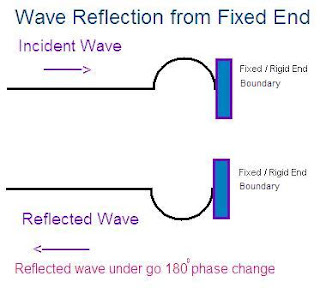
If the displacement of particles in incident pulse is upward, then the displacement of particles in reflected pulse is downward and vice versa. This mean wave or pulse reflected from a rigid boundary , it undergos a phase change of 180 degree.
If the equation for incident wave, propagated along +ve X axis :
y = A sin (wt - kx)
Then the equation for wave reflected from rigid end will be
y = A' sin (wt + kx + π )
Here A' is the amplitude of the reflected wave
(x) is replaced by (-x) because reflected wave travel in opposite direction
( π ) is the phase difference between incident and reflected wave.
Production of Stationary wave
When two waves of same frequency and Amplitude travel in opposite direction in a straight line, at the same speed, they superimpose each other and a new wave is formed. It is called Stationary wave.
Further READING in Stationary wave
Nodes & Anti Nodes
At some points, particles of medium always remain at their mean position. Such points are called Nodes.
The position of t he particles which vibrate with maximum amplitude are called Anti Nodes.
Differentiate close and open pipe in sound wave?
A pipe close at one end is called a closed pipe. When stationary wave is formed with in the pipe, an Anti – node is formed always at the open end.
In case of closed pipe, a node is formed at the closed end, the wave get reflected by the rigid wall at closed end.
Sonic BOOM
The Pressure waves produced by airplanes, as they travel Super sonic (Greater than Sound velocity )
As the plane travel, it pushes the air surrounding it. which courses pressure waves
These shock waves surrounding the plane is sonic boom.
Sonic Boom: Youtube video
Video by Sciencemadefun
Tuesday, March 1, 2011
Plus one Physics : Previous question papers
First Year Improvement / SAY question paper August 2014 NEW
Plus one Physics Model Question paper 2011 ( Attingal Cluster group)
One , Two , Three, Four
Adding more... very soon
Post URL , if you find any useful link
